
1. Background of GMP
In the United States in the early 20th century when the industry was still aboriginal (ice was used for refrigeration, and milk was also unsterilized). Preservative chemicals and food additives are arbitrarily used without supervision. The drug contains heroin, cocaine and morphine with no warning on the label.
In 1937 the SE Massengill Company manufactured the drug Sulfanilamide to treat streptococcal infections. They used the chemical diethylene glycol (antifreeze) as a solvent and as a result, many people suffered kidney failure, or anaphylaxis and death
Before 1962 another tragedy was Thalidomide, a sedative and pain reliever. There are also no warnings for use in pregnant women. Causing children to be born with severe deformities in Europe, Canada…
And in 1962 the GMP standard was enacted in the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act for products: food, drugs, cosmetics and medical devices.
2. What is GMP?
GMP (short for Good Manufacturing Practices) is a set of principles and standards for the manufacture of drugs and medicinal ingredients to ensure that drugs and medicinal ingredients are consistently produced and tested according to quality standards. The quantity is suitable for use and the requirements of the certificate of free sale of drugs and medicinal ingredients.

3. Role of GMP
- Legal
The Ministry of Health stipulates that all pharmaceutical production and business establishments are required to be GMP-certified. Therefore, GMP standards play the role of a mandatory prerequisite to help businesses comply with the law and be able to circulate their products on the legal market.
- Benefits for businesses:
- Building trust, gaining approval from partners and customers, helping to increase consumption of products and services
- Ensuring products and services are safe and stable in quality to help reduce the rate of product recalls and negative feedback
- Employees understand their roles and responsibilities at work to increase work efficiency
- A competitive advantage compared to competitors’ products to help businesses stand firm and penetrate new markets
- Benefits to consumers:
- Helping consumers access high-quality products with reasonable prices
- GMP helps consumers choose products with clear and safe origin
- Reduce the situation of counterfeit goods, imitation goods, poor quality goods, smuggled goods
4. The GMP Certificates
– Popular GMP certificates:
- EU GMP: EU-GMP Certificate: issued by the pharmaceutical regulatory authorities of EMA member countries (European Medicines Agency)
- PIC/S-GMP: PIC/S-GMP Certificate: issued by a pharmaceutical regulatory authority that is a member of the PIC/S (Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme)
- WHO-GMP: WHO-GMP Certificate: issued by the Drug Administration of Vietnam
- Japan GMP: Japan GMP Certificate: issued by the Japan Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)

– In Vietnam, factories are meeting GMP standards as follows:
- EU-GMP Certificate: Pymepharco, Imexpharm, Savipharm, Tenamyd, Medochemie,…
- PIC/S-GMP Certificate: Korea United Pharm, Kyongbo Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Fresenius Kabi Viet Nam,…
- WHO-GMP Certificate: Bidiphar, United International Pharma, OPC, Domesco,…
- Japan GMP Certificate: DHG, RohtoMentholatum, Nipro Pharm, Santen Pharmaceutical,…
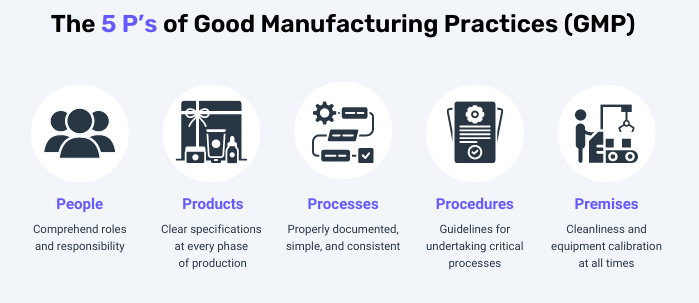
5. Basic contents of GMP
– GMP covers all aspects that can affect the quality of pharmaceutical products. It mainly includes
- People:
- It is necessary to clarify the roles and responsibilities of each employee
- Need to follow the procedure
- Be trained and evaluated for assigned work
- Premises and Equipment:
- Validated and calibrated for intended use
- Have operating procedures, maintenance schedules, cleaning and related documentation
- Designed to facilitate cleaning
- Cross-contamination design
- Processes:
- The steps must be specified
- Processes are clearly defined, consistent, and documented
- The control for major changes is always prepared
- Procedures:
- Needs to be documented and archived
- Covering the entire process
- Ensure all irregularities are investigated and reported
- Products:
- Specify raw materials, ingredients, semi-finished products and finished products
- There are methods for research, development, process, production and packaging, testing, sampling, status control, stability testing and record storage.
Basic contents of EU-GMP on manufacturing finished drugs
- Pharmaceutical Quality System
- Personnel
- Premise and Equipment
- Documentation
- Production
- Quality control
- Outsourced activities
- Complaints and Product Recall
- Self Inspection
Annexes
Annex: Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products
Annex: Manufacture of Biological active substances and Medicinal Products for Human Use
Annex: Manufacture of Radiopharmaceuticals
Annex: Manufacture of Medicinal Gases
Annex: Manufacture of Herbal Medicinal Products
Annex: Sampling of Starting and Packaging Materials
Annex: Manufacture of Liquids, Creams and Ointments
Annex: Manufacture of Pressurised Metered Dose Aerosol Preparations for Inhalation
Annex: Computerised Systems
Annex: Use of Ionising Radiation in the Manufacture of Medicinal Products
Annex: Manufacture of Investigational Medicinal Products
Annex: Manufacture of Products derived from Human Blood or Human Plasma
Annex: Qualification and validation
Annex: Certification by a Qualified Person and Batch Release
Annex: Parametric release
Annex: Reference and Retention Samples
Annex: Importation of medicinal products
References
- Determination No. 3886/2004/QĐ-BYT
- Circulars 35/2018/TT-BYT
- Eudralex – Volume 4
- https://dav.gov.vn/danh-sach-cac-nuoc-ich-pics-n534.html




