
Research and development of many new drugs open up treatment opportunities and change the lives of millions of patients. However, developing and manufacturing new drugs is a very difficult process, requiring a lot of research time, equipment, resources, and huge costs.
1. More than a decade path for a new drug to be born
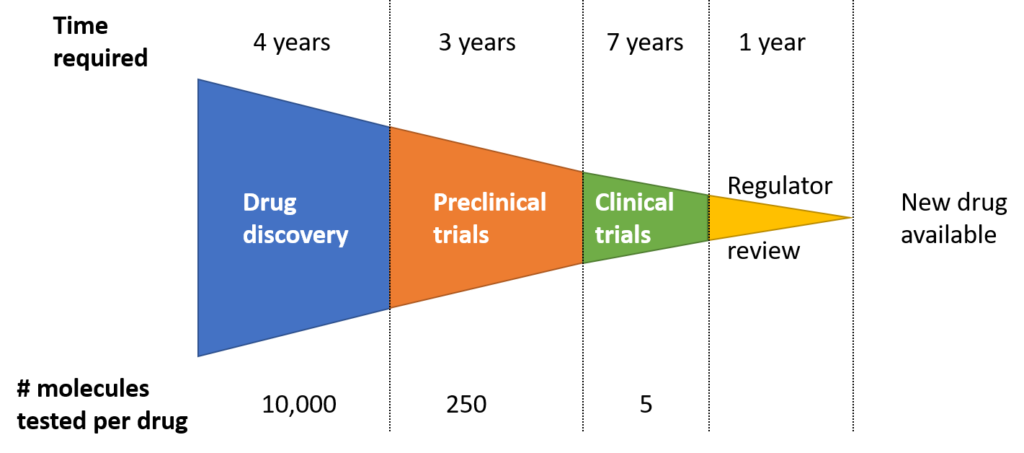
Every year around the world, several dozen new drugs are licensed for use, but before that tens of thousands of candidate drugs have been discarded. Finding, developing, and manufacturing new drugs is a complex and time-consuming process. On average, the process from R&D to market release will take about 10-15 years and cost more than $1 billion.
Finding a new therapeutic drug requires tremendous resources, excellent scientific ideas, and the persistent efforts of scientists. The results of the introduction of new drugs are enormous, which will bring hope, treatment opportunities, and change the lives of millions of patients.
2. What is the process of making new drugs?
The drug manufacturing process must follow a certain sequence. According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the drug development and manufacturing process consists of 5 basic steps as follows:
2.1. Drug discovery and development
Before drug discovery, scientists must delve into the pathogenesis at the molecular level. This is the basis for searching and developing compounds that are capable of activating/inhibiting the target. Only a few potential compounds meet the criteria for further research from the thousands of compound libraries. This process takes a lot of time and resources. Therefore, with the development of the computer industry, in silico virtual screening software is designed and used to quickly screen huge libraries of compounds, identify the compounds with the most potential activity on the target. These potential compounds will also be investigated for activity through in vitro and in vivo tests to identify a compound with real therapeutic activity. Once researchers have identified a compound with growth potential, they will conduct information-gathering experiments including:
- The process of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of this substance
- The potential benefits and mechanism of action of the active ingredient
- Dosage, administration, side effects, interactions with other drugs
- How the active ingredient being studied affects people of different genders, races, etc.
- Efficacy of the studied active ingredient with similar drugs.
After having a deep understanding of the research-active ingredient (drug substance), determining the desired dosage form, the research phase to find the most optimal dosage-manufacturing formula is carried out.
– Research on the incompatibility of active ingredients and excipients: The aim is to select excipients that can be used in the formulation. With different dosage forms, there are different test methods, but the general principle is to create contact between active ingredients and excipients, leave them in aging conditions to observe the change compared to the control sample (only active ingredients). Incompatibility occurs when the sample is discolored, too moist, has an unpleasant odor, etc. compared with the control sample under the same conditions.
– Investigation of formulas – initial production process: The aim is to determine a preliminary formula including the ingredients and respective volume. The survey is always prioritized in the following order: The simplest, least ingredient formula – The simplest production process – Evaluation criteria (evaluate physical standards, easy to do first; if successful, conduct chemical criteria to save time and research costs).
– Formula optimization: The purpose is to find out the formula, parameters (conducting conditions) of the process so that the products produced meet the quality standards as directed.
– Manufacturing process development – scale-up – process validation: This is an important step in pharmaceutical research (formula and manufacturing process). Manufacturing process development is carried out in the following steps: Testing to select the right manufacturing method – Producing on a pilot scale – Pilot-scale production and process validation – Production and validation process at production scale. The purpose is to create products that meet the quality requirements and ensure the maintenance and uniformity between commercial production batches.
– Developing and evaluating standards: A set of quality standards includes: Standards – Methods – Validation of analytical methods (protocol, report, and raw data) – Test sheet – Standard description standard.
– Packaging development and stability research: The selection of packaging will usually be based on dosage form as well as references from products already available on the market. Stability research can be consulted from official sources such as ICH Q1A (R2), ASEAN Guidelines (Asean Guideline On Stability Study Of Drug Product), Circular 32/2018/TT-BYT, etc.
2.2. Preclinical research
Before testing a drug on people, researchers must perform preclinical studies to determine whether the drug is likely to cause toxicity. Two trials are required for preclinical studies: in vitro and in vivo.
In vitro is a research method, performed on biological molecules and cells cultured in the laboratory. Meanwhile, in vivo is a method to study the effects of drugs on living organisms, usually animals such as mice, rabbits,…
Preclinical studies will provide information on dosage, toxicity, and drug-cell interactions. Based on this information, researchers will consider whether the active ingredient under study should continue to be tested in humans.
2.3. Clinical research
Clinical research is studies of the effects of drugs directly on people. The clinical research process includes the following steps:
– Clinical research design
– Phases of clinical trials of drugs before being marketed: The clinical trial phase of drugs usually goes through the following stages:
- Submit to regulatory authorities for clinical trial licensing
- Conducting clinical research: After getting permission from the regulatory agency, clinical research on the drug will be conducted and carried out through 4 phases.
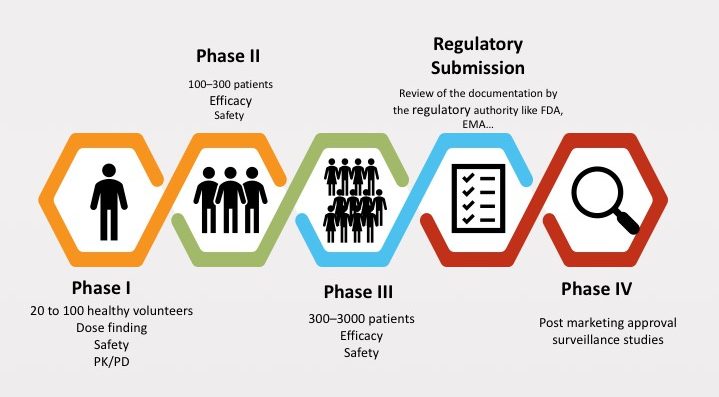
Throughout the research phases, the regulatory agencies will conduct monitoring to ensure objectivity and integrity, as well as the safety of the participants.
2.4. Apply for a license to produce and circulate drugs from a regulatory agency
To apply for marketing authorization for a drug, the drug manufacturer must submit a complete set of data, including: the discovery and development process of the drug, and scientific information proving the effectiveness and safety of the drug through the results. Preclinical and clinical research results, dosage form, manufacturing process, drug labeling,…
The expert panel from the regulatory agency will evaluate the registration dossier to decide whether to license the drug production and circulation or not.
2.5. Monitoring the safety of drugs after they are on the market
After passing phase 3 of clinical trials, the manufacturer was able to apply for a marketing license for the product, at this time the drug has only been used on a few thousand patients. Therefore, the actual safety and effectiveness of the drug are monitored and determined after several years of the drug being marketed to a large number of users. Therefore, the regulatory agency will continue to monitor the issues related to the circulation of the drug, collect reports on the drug to give timely instructions in case of adverse drug reactions.
References:
https://www.cern-foundation.org/education/clinical-trials/clinical-trial-phases
https://www.fda.gov/patients/learn-about-drug-and-device-approvals/drug-development-process
https://sruk.org.uk/the-drug-discovery-process/





You must be logged in to post a comment.